Geral
Editorial do WSJ
Obama's ploy means the highest capital gains tax rate since 1978
Remember the moment in 2008 when Charlie Gibson of ABC News asked Senator Barack Obama why he would support raising the capital gains tax even though "revenues from the tax increased" when the rate fell? Mr. Obama's famous reply: "I would look at raising the capital gains tax for purposes of fairness." Well, we were warned.
Here we are four years later, and President Obama on Tuesday night linked the term "fair" to U.S. tax and economic policy seven times. The U.S. economy is still hobbling out of recession, real family incomes are falling and 14 million Americans are unemployed, but Mr. Obama declared that his top priority is not to reform the tax code to promote growth and job creation. His overriding goal is redistributing income.
Mr. Obama endorsed the political ruse he calls the Buffett rule, which asserts as a matter of moral principle that millionaires should not pay a lower tax rate than middle-class wage earners. Specifically, Mr. Obama is proposing that anyone earning more than $1 million pay at least 30% of that income to Uncle Barack.
The White House says that if a millionaire household's effective tax rate falls below 30%, it would have to pay a surcharge—in essence a new Super Alternative Minimum Tax—to bring the tax liability to 30%. For those facing this new Super AMT, all deductions and exemptions would be eliminated except for charity.
The Buffett rule is rooted in the fairy tale that taxes on the wealthy are lower than on the middle class. In fact, the Congressional Budget Office notes that the effective income tax rate of the richest 1% is about 29.5% when including all federal taxes such as the distribution of corporate taxes, or about twice the 15.1% paid by middle-class families. (See "How Much the Rich Pay," January 23, 2012.)
This is because wealthy tax filers make most of their income from investments. Such income is taxed once at the corporate rate of 35% and again when it is passed through to the individual as a capital gain or dividend at 15%, for a highest marginal tax rate of about 44.75%.
This double taxation is one reason the U.S. has long had a differential tax rate for capital gains. Another reason is because while taxpayers must pay taxes on their gains, they aren't allowed to deduct capital losses (beyond $3,000 a year) except against gains in the current year. Capital gains also aren't indexed for inflation, so a lower rate is intended to offset the effect of inflated gains.
One implication of the Buffett rule is that all millionaire investment income would be taxed at the shareholder level at a minimum rate of 30%, up from 15% today. The tax rate on investment income from corporations would rise to 54.5% from 44.75%, a punitive tax on start-up or expanding businesses.
The new 30% capital gains rate would be the developed world's third highest behind only Denmark and Chile, according to the American Council for Capital Formation. This is on top of the 35% corporate rate that is already the second highest rate in the world after Japan. That giant sucking sound you hear come January 2013 would be hundreds of billions of investment dollars fleeing to China, India, Korea and other U.S. competitors. Lower capital investment in the U.S. means less wage growth, and so the people hurt most by this tax hike would be workers, according to a study by the Institute for Research on the Economics of Taxation.
Mr. Obama conceded on Tuesday that the high U.S. corporate tax is an economic loser. Yet he misses the crucial point that business owners assess the combined corporate and capital gains tax on those business profits. Lowering the corporate tax rate makes the U.S. more competitive, but the tax change is self-defeating if it is combined with an even larger rise in investment income taxes on capital gains and dividends.
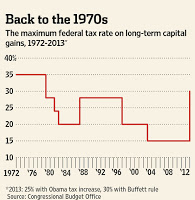
Mr. Obama isn't setting himself apart merely from conservatives with this Buffett ploy. He is rejecting 35 years of bipartisan tax policy that began with the passage of the Steiger Amendment by a Democratic Congress that cut the capital-gains rate to 28% from 35% in 1978.
As the nearby chart shows, the rate has never since risen above 28%, and the last time it moved that high was in 1986 as part of the Reagan-Rostenkowski tax reform that also cut the top marginal income tax rate to 28% from 50%. With income-tax rates so low, a differential was arguably less necessary—though it's worth noting that capital gains revenues fell dramatically after that rate increase.
A decade later Bill Clinton agreed to cut the rate back to 20% as part of the balanced-budget deal with Newt Gingrich. Capital gains revenues soared, helping to balance the federal budget. Nearly every study estimates that the revenue-maximizing tax rate from the capital gains tax is between 15% and 28%. Doug Holtz-Eakin, the former director of the Congressional Budget Office, says that a 30% tax rate "is almost surely above the rate that maximizes tax revenues." So it's likely the Buffett trick would lose revenue for the government.
Yet in a time of the highest deficits since World War II, Mr. Obama wants to double the capital gains tax rate even as he raises the top income-tax rate to 42% or so. Mr. Obama really is taking us back to the worst habits of the 1970s. And not because he thinks higher rates will raise revenue, but merely so he can score points against Mitt Romney and stick it to the successful.
This isn't tax fairness. It's tax folly.
- Mr. Buffett's Tax Secrets
Editorial do WSJ The least he can do is show Americans why he pays so little Warren Buffett has forcefully injected himself into the U.S. political debate, with President Obama using the billionaire's anecdote that he pays a lower tax rate than his...
- Hunting The Rich
The Economist THE horns have sounded and the hounds are baying. Across the developed world the hunt for more taxes from the wealthy is on. Recent austerity budgets in France and Italy slapped 3% surcharges on those with incomes above €500,000 ($680,000)...
- The Spend Now, Tax Later Jobs Bill
By ALAN REYNOLDS, WSJ The president's "Plan for Economic Growth and Deficit Reduction" mainly hinges on persuading Congress to trade $447 billion in temporary payroll tax cuts and spending increases—the "jobs plan"—for permanent income-tax increases...
- The 2013 Tax Cliff
Editorial do WSJ President Obama unveiled part two of his American Jobs Act on Monday, and it turns out to be another permanent increase in taxes to pay for more spending and another temporary tax cut. No surprise there. What might surprise Americans,...
- Warren Buffett's Tax Dodge
The billionaire volunteers the middle class for a tax increase. Editorial do WSJ Barney Kilgore, the man who made the Wall Street Journal into a national publication, was once asked why so many rich people favored higher taxes. That's easy, he replied....
Geral
The Buffett Ruse

Editorial do WSJ
Obama's ploy means the highest capital gains tax rate since 1978
Remember the moment in 2008 when Charlie Gibson of ABC News asked Senator Barack Obama why he would support raising the capital gains tax even though "revenues from the tax increased" when the rate fell? Mr. Obama's famous reply: "I would look at raising the capital gains tax for purposes of fairness." Well, we were warned.
Here we are four years later, and President Obama on Tuesday night linked the term "fair" to U.S. tax and economic policy seven times. The U.S. economy is still hobbling out of recession, real family incomes are falling and 14 million Americans are unemployed, but Mr. Obama declared that his top priority is not to reform the tax code to promote growth and job creation. His overriding goal is redistributing income.
Mr. Obama endorsed the political ruse he calls the Buffett rule, which asserts as a matter of moral principle that millionaires should not pay a lower tax rate than middle-class wage earners. Specifically, Mr. Obama is proposing that anyone earning more than $1 million pay at least 30% of that income to Uncle Barack.
The White House says that if a millionaire household's effective tax rate falls below 30%, it would have to pay a surcharge—in essence a new Super Alternative Minimum Tax—to bring the tax liability to 30%. For those facing this new Super AMT, all deductions and exemptions would be eliminated except for charity.
The Buffett rule is rooted in the fairy tale that taxes on the wealthy are lower than on the middle class. In fact, the Congressional Budget Office notes that the effective income tax rate of the richest 1% is about 29.5% when including all federal taxes such as the distribution of corporate taxes, or about twice the 15.1% paid by middle-class families. (See "How Much the Rich Pay," January 23, 2012.)
This is because wealthy tax filers make most of their income from investments. Such income is taxed once at the corporate rate of 35% and again when it is passed through to the individual as a capital gain or dividend at 15%, for a highest marginal tax rate of about 44.75%.
This double taxation is one reason the U.S. has long had a differential tax rate for capital gains. Another reason is because while taxpayers must pay taxes on their gains, they aren't allowed to deduct capital losses (beyond $3,000 a year) except against gains in the current year. Capital gains also aren't indexed for inflation, so a lower rate is intended to offset the effect of inflated gains.
One implication of the Buffett rule is that all millionaire investment income would be taxed at the shareholder level at a minimum rate of 30%, up from 15% today. The tax rate on investment income from corporations would rise to 54.5% from 44.75%, a punitive tax on start-up or expanding businesses.
The new 30% capital gains rate would be the developed world's third highest behind only Denmark and Chile, according to the American Council for Capital Formation. This is on top of the 35% corporate rate that is already the second highest rate in the world after Japan. That giant sucking sound you hear come January 2013 would be hundreds of billions of investment dollars fleeing to China, India, Korea and other U.S. competitors. Lower capital investment in the U.S. means less wage growth, and so the people hurt most by this tax hike would be workers, according to a study by the Institute for Research on the Economics of Taxation.
Mr. Obama conceded on Tuesday that the high U.S. corporate tax is an economic loser. Yet he misses the crucial point that business owners assess the combined corporate and capital gains tax on those business profits. Lowering the corporate tax rate makes the U.S. more competitive, but the tax change is self-defeating if it is combined with an even larger rise in investment income taxes on capital gains and dividends.
Mr. Obama isn't setting himself apart merely from conservatives with this Buffett ploy. He is rejecting 35 years of bipartisan tax policy that began with the passage of the Steiger Amendment by a Democratic Congress that cut the capital-gains rate to 28% from 35% in 1978.
As the nearby chart shows, the rate has never since risen above 28%, and the last time it moved that high was in 1986 as part of the Reagan-Rostenkowski tax reform that also cut the top marginal income tax rate to 28% from 50%. With income-tax rates so low, a differential was arguably less necessary—though it's worth noting that capital gains revenues fell dramatically after that rate increase.
A decade later Bill Clinton agreed to cut the rate back to 20% as part of the balanced-budget deal with Newt Gingrich. Capital gains revenues soared, helping to balance the federal budget. Nearly every study estimates that the revenue-maximizing tax rate from the capital gains tax is between 15% and 28%. Doug Holtz-Eakin, the former director of the Congressional Budget Office, says that a 30% tax rate "is almost surely above the rate that maximizes tax revenues." So it's likely the Buffett trick would lose revenue for the government.
Yet in a time of the highest deficits since World War II, Mr. Obama wants to double the capital gains tax rate even as he raises the top income-tax rate to 42% or so. Mr. Obama really is taking us back to the worst habits of the 1970s. And not because he thinks higher rates will raise revenue, but merely so he can score points against Mitt Romney and stick it to the successful.
This isn't tax fairness. It's tax folly.
- Mr. Buffett's Tax Secrets
Editorial do WSJ The least he can do is show Americans why he pays so little Warren Buffett has forcefully injected himself into the U.S. political debate, with President Obama using the billionaire's anecdote that he pays a lower tax rate than his...
- Hunting The Rich
The Economist THE horns have sounded and the hounds are baying. Across the developed world the hunt for more taxes from the wealthy is on. Recent austerity budgets in France and Italy slapped 3% surcharges on those with incomes above €500,000 ($680,000)...
- The Spend Now, Tax Later Jobs Bill
By ALAN REYNOLDS, WSJ The president's "Plan for Economic Growth and Deficit Reduction" mainly hinges on persuading Congress to trade $447 billion in temporary payroll tax cuts and spending increases—the "jobs plan"—for permanent income-tax increases...
- The 2013 Tax Cliff
Editorial do WSJ President Obama unveiled part two of his American Jobs Act on Monday, and it turns out to be another permanent increase in taxes to pay for more spending and another temporary tax cut. No surprise there. What might surprise Americans,...
- Warren Buffett's Tax Dodge
The billionaire volunteers the middle class for a tax increase. Editorial do WSJ Barney Kilgore, the man who made the Wall Street Journal into a national publication, was once asked why so many rich people favored higher taxes. That's easy, he replied....
